Solvents VOC Inventories

Looking Back
The first National Emission Ceiling Directive (NECD) was adopted in 2001. It requested Member States to report their emission inventories for the main pollutants to the EU. However, a common approach was lacking, and industry felt that many inventories were overestimating the VOC emissions from solvents. That is why ESIG decided to develop its own inventories in 2008 and 2009. Since 2015, we have collected data and published our solvents VOC inventories annually.
National Emission Ceiling Directive (2016/2284/EU)
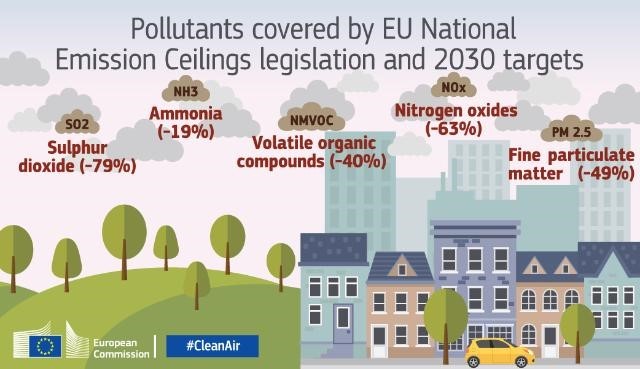
The current National Emissions Ceilings (NEC) Directive entered into force in 2016 and sets 2020 and 2030 emission reduction commitments for five main air pollutants:
-
-
- nitrogen oxides (NOx),
- non-methane volatile organic compounds (NMVOCs),
- sulphur dioxide (SO2),
- ammonia (NH3)
- and fine particulate matter (PM2.5).
-
The Directive ensured that the emission ceilings for 2010 set in the earlier directive remained from 2001 applicable for Member States until the end of 2019. The EU law while transposing the reduction commitments for 2020 agreed by the EU and its Member States in the 2012, revised the Gothenburg Protocol under the Convention on Long-range Transboundary Air Pollution (CLRTAP).
The 2020 emission reduction targets for volatile organic compounds in the EU were already reached in 2017!
ESIG inventories
Since 2015, we have collected data and published the inventories annually. Our inventories are based on real data coming from solvents’ sales and can be consulted by EU Member States when establishing their own inventories. Since 2016, ESIG VOC inventories are recognized as a valid source in the joint EMEP/EEA air pollutant emission inventory guidebook. The guidebook provides advice on how to report emissions data under the UNECE Convention on Long-range Transboundary Air Pollution (CLRTAP) and the EU National Emission Ceilings Directive.
What are the big trends with respect to VOC emissions?
The European Environmental Agency reports that since 1990, emissions of non-methane volatile organic compounds (NMVOC) have decreased by 59% in EEA countries and 62 % in the EU27+UK. Further breakdown shows that more than half of the reduction was achieved in the 90’s. Since then, the rate of reduction has been decreasing and for the last 5 years, the emissions seem to have stabilised. As all sectors sought to reduce its VOC emissions, the 2020 ceilings set in the National Emissions Ceilings Directive were achieved already in 2017.
For the solvents part in those NMVOC emissions, a reduction of 49% between 1990 and 2018 and 27% since 2005 can be observed. So, when it comes to “solvents & product use”, the emissions have been reduced to almost half of 1990 emission levels. Important EU regulatory measures, such as the Solvent Emissions Directive (1999) — now part of the Industrial Emissions Directive (2010) and the Paints Directive (2004) — were introduced and have contributed to reductions in the solvent content of products and emissions from industries using solvents. Hence the stabilisation for solvents VOC emissions has started slightly earlier, and no substantial reductions can be noted since 2013.
In parallel to these outstanding reductions, the solvents VOC emission has proportionally become one of the biggest contributing categories. The largest source of current NMVOC emissions is the ‘Solvent and product use’ sector which includes a multitude of different processes and products.
VOC emissions from biogenic sources are not included in those anthropogenic emission inventories. Biogenic VOC emissions may vary with future climate change patterns and, in some regions, be a major fraction of the atmospheric burden of hydrocarbons during ozone episodes.
Are solvents still needed?
Yes, solvents deliver key benefits to society in allowing an optimization of processes and in maintaining undisputed product performances. Solvents are crucial in many different processes and products as they are simply needed to let them perform their function. Solvents provide solutions in many sectors from coating vehicles to manufacture of tyres or are used in cleaning agents and diverse printing applications.
In pharmaceutical industry they are necessary to achieve purity required for modern medicine or they serve as process chemicals in the production of active ingredients in contrast media to detect cancer or leukaemia. Alcohols are used in the manufacturing of disinfectants and hand gels.
By far the biggest application field are coatings. Outdoor paints and coatings must be durable enough to withstand the heat of summer, freezing rain, melting snow and it is because of solvents, they can. Paints made with solvents stay brilliant and strong in some of the toughest weather conditions. Without proper protection, metals exposed to the outdoors will inevitably experience corrosion. Solvent-based paints for metals offer the most resilient, long-lasting protection. They are essential to maintain the integrity of critical infrastructure like bridges and pipelines for decades to come. Blends of solvents are used to achieve optimum solvency or to regulate the evaporation and hence drying time.
Are further VOC reductions from solvents realistic?
The solvent industry has always been a front runner in optimizing its solvent use. Innovation started early and the industry was the first sector to drastically reduce its VOC emissions. The industry continues anticipating policy trends toward sustainability and complying with the strict legislative framework related to health and environmental protection.
Industry is constantly working towards technical and economic solutions and VOC emissions have already been optimized in processes and products.
However, it is still not technically feasible in most cases to remove all VOCs while retaining process or product performance. All uses are necessary applications where solvents fulfill their dedicated function. Due to the need for solvents in industrial processes and in daily life, VOC emission from solvents will always be present to a certain degree.
It is interesting to note that over the last decades, solvent sales have not been declining, meaning solvents are used in those applications that need them, but at the same time emissions have declined and have now stabilized.
Industrial processes are cleaned up to the maximum level by applying the best available abatement techniques, thus contributing to lower emission factors. Implications of the updated STS BREF will need to be analyzed once it has been fully implemented throughout all Member States (2024).
Recently the presence of solvents in several application fields is also measured against sustainability criteria, such as comparing short term emission versus emissions from Life Cycle Analysis point of view.

Looking ahead
ESIG has just published its 2020 Solvents VOC inventories and will continue to issue them each year. We will also foster research on VOCs, on ozone precursors and help to improve air quality.